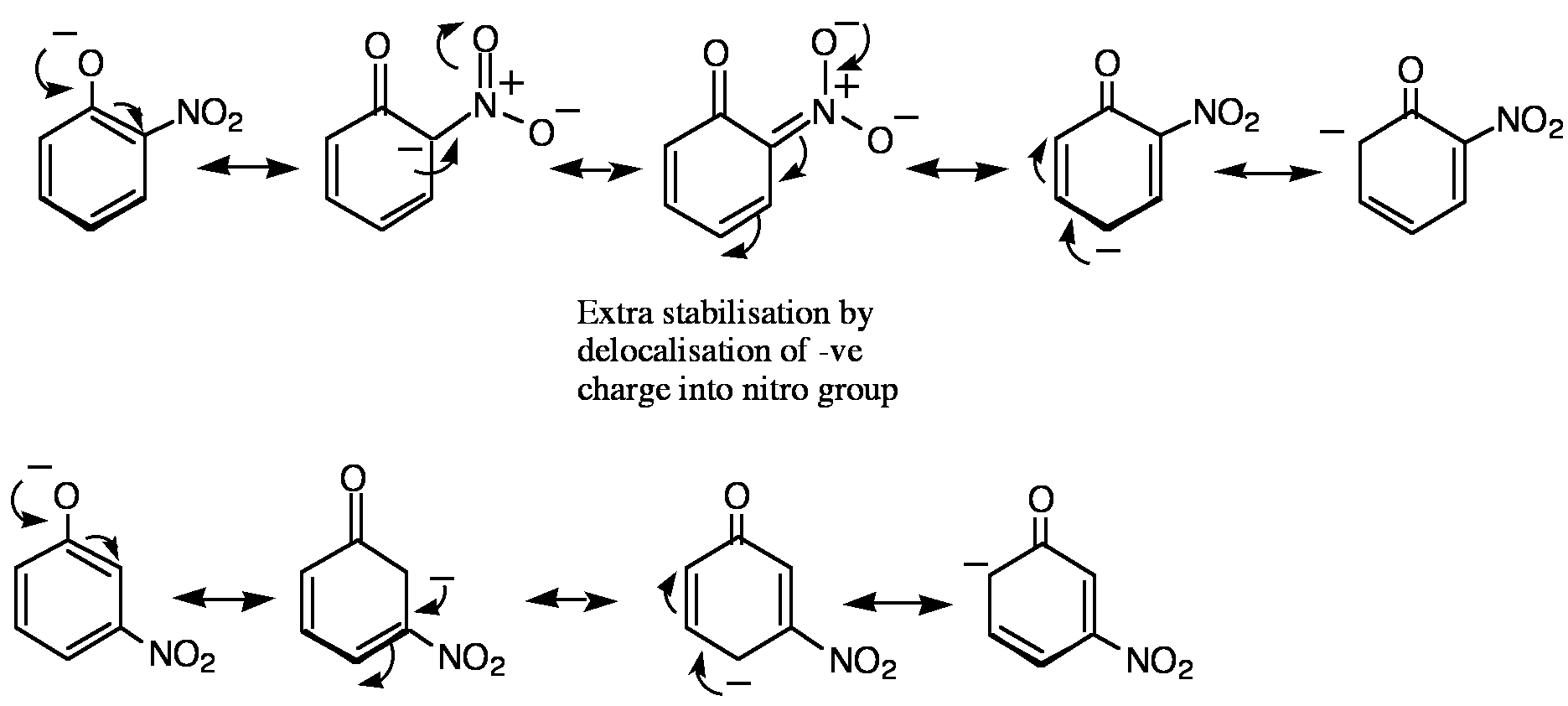
Red regions are electron rich (negative) and blue regions are electron depleted (positive). Note where the red regions are in each of these phenoxide anions. Are the negative charges localised on the phenolic oxygen or delocalised onto the nitro groups?
The more delocalised the anion, the more stable it will be and hence the more acidic the corresponding phenol.
2-Nitrophenoxide |
3-Nitrophenoxide |
4-Nitrophenoxide |

Hydrogen | Fluorine | Methane | Ethylene | Acetylene | Allene | Benzene | p-orbitals | d-orbitals | f-orbitals