Reagents:
Serum samples A, B and C from smokers, passive smokers and non-smokers
PBS (phosphate buffered saline)
Stock cotinine solution (500 µg/litre in PBS)
PBS-Tween (PBS containing 0.05% Tween-20)
First antibody (rabbit anti-cotinine) in PBS + 1% dried milk protein
Second antibody (peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG) in PBS + 1% dried milk protein)
Substrate reagent (0.04% o-phenylenediamine, 0.02% hydrogen peroxide in 80 mM citrate buffer pH 5.0)
12.5% H2SO4
Procedure: (WORK IN PAIRS)
Make sure you have read and understood the theory behind competitive ELISA before proceeding with this experiment.
ELISA tests are commonly carried out in 96-well plates which can be processed automatically. Sample plates will be available in the lab for inspection. Each pair of students is provided with two 8-well strips which will be processed manually. Wells 2 to 8 in these strips have already been treated overnight with cotinine attached to a synthetic protein (polylysine). Well 1 (a negative control) was treated with buffer. The excess cotinine was then removed and all 8 wells blocked with PBS (phosphate buffered saline) containing 1% dried milk protein. The strips are provided to you with the blocking solution still in place. (Dried milk protein is used to saturate all the remaining protein binding sites in the wells simply because it is cheap!).
Note: Each student in each pair should be responsible for one of the two strips. One strip will be used to construct a standard "calibration" curve, the other will be used for the test serum samples.
- Collect two 8-well strips. These are provided with blocking solution in them. Remove the blocking solution from each well of both strips by suction (apparatus will be demonstrated).
- Pipette 100 µl of PBS-Tween into each well of both strips. Remove again by suction. Repeat this procedure twice more. (The wells are now "washed" free of all unbound protein). Put the strips to one side while you prepare a series of standard solutions in test tubes.
- Using the 500 µg/litre stock cotinine solution, prepare a series of standard solutions in small plastic test tubes to give the following 7 concentrations by diluting the stock with PBS. Each standard dilution should have a final volume of 0.5 ml. (Only one set per pair required).
Standards: 500, 200, 100, 75, 50, 25 and 0 µg/litre cotinine
- Take the first strip and carefully pipette 10 µl of PBS into well 1 and 10 µl of the 7 standards into wells 2 to 8 (one standard per well, the 500 µg/l in well 2, the 200 µg/l in well 3 etc. — see figure below)
- Take the second strip, and carefully pipette 10 µl PBS into well 1, 10 µl of serum A into wells 2 and 3, 10 µl serum B into wells 4 and 5, 10 µl serum C into wells 6 and 7 and 10 µl PBS into well 8. Together, your two well strips should be as in the figure below, with sera A, B and C being measured in duplicate:
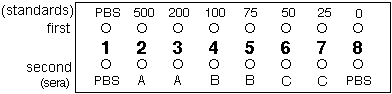
- Now add 40 µl first antibody solution to all 8 wells of both strips and incubate at room temperature for 20 min. Tap the strips gently every 2-3 min to help mix the contents.
- After 20 min, remove the first antibody by suction and wash each well twice with PBS-Tween using the procedure described in Step 3.
- Add 50 µl second antibody solution to each well and incubate for 10 min at room temperature with occasional gentle mixing by tapping.
- After 10 min, remove the second antibody by suction and wash each well twice with PBS-Tween using the procedure described in Step 2.
- Add 75 µl substrate reagent to each well of the first strip only and tap to mix.
- Watch the colour develop for exactly 1 min (continue tapping) then quickly but carefully add 75 µl 12.5% H2SO4 to each well to fix the colour.
- Repeat steps 10 and 11 for the second strip. Both strips must be incubated for exactly the same time.
- Estimate the cotinine concentrations in sera A, B and C by eye by reference to the standards, then determine which of the samples represent the smoker, passive smoker and non-smoker. Complete the table below. (In the clinical laboratory, a special colorimeter called a "plate reader" would be used to give a quantitative estimate of cotinine concentration.

