Micro X-ray CT: How it works
X-ray CT is a method to image the 3D volume of a sample and show differences in x-ray attenuation of the materials. The Zeiss Xradia Versa 620 is an X-ray Microscope(XRM) and X-ray Computed Tomography (X-ray CT) scanner capable of achieving sub-micron resolution. It offers three imaging modes, absorption contrast, absorption contrast with phase enhancement, and labDCT grain orientation analysis.
Absorption X-ray CT
Materials differ in their x-ray attenuation (often simplified called x-ray absorption) properties. X-ray CT creates a series of projection images by illuminating the sample over 360 degrees. The projection images are then processed by an algorithm that computes a tomographic 3D volume (hence X-ray Computed Tomography).
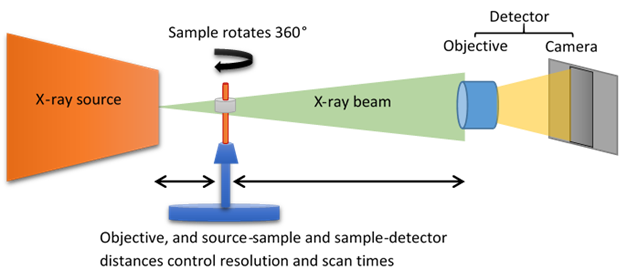
Figure 1: Schematic drawing of the X-ray CT acquisition
Phase contrast
In addition to absorbing x-rays, material boundaries also introduce a phase shift to the x-ray beam. Under certain conditions, this phase shift can be seen as a phase fringe on boundaries and enhances visibility of such thin features. In the Zeiss Xradia Versa, this type of propagation phase contrast is an effect of the optical arrangement and is strongest for low-absorbing materials imaged at a high resolution. It can be enhanced with certain imaging conditions to aid with visualisation of thin boundaries.
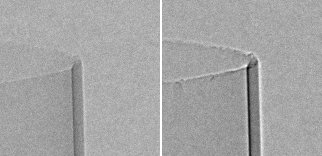
Fig 2. Left: Image with little phase contrast. Right: Image with enhanced phase contrast.
LabDCT
The instrument is equipped with a novel Laboratory Diffraction Contrast Tomography (LabDCT) module, which makes it possible to collect 3D diffraction patterns from intact polycrystalline samples. Special grain reconstruction software (XNovo GrainMapper3D) can then be used to determine grain orientation and grain volume without having to section the sample.
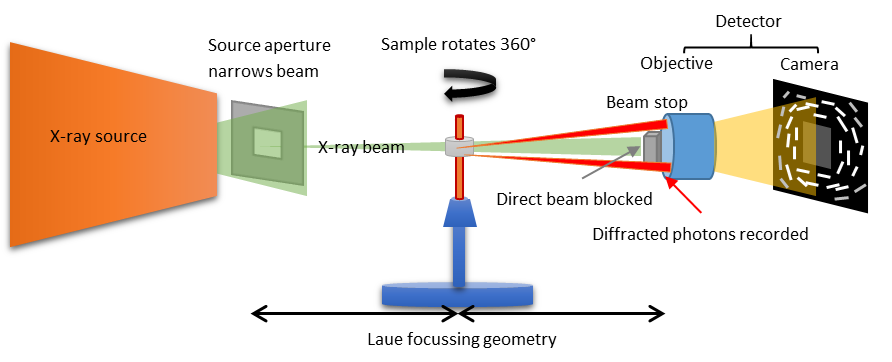
Figure 3: Schematic drawing of the LabDCT acquisition setup
Sample requirements
Samples size can range from microns to 50 mm diameter, depending on sample material. Ideally samples have a cylindrical shape and are mounted upright. Samples need to be stable and not move for the duration of the scan, which is generally between 1 hour and over 24 hours. High resolution, and highly absorbing materials, lead to longer scan durations. No special surface treatment is required, however biological samples and samples containing liquid need to be encased in leak-proof containers.
Currently samples suitable for LabDCT should be single-phase (poly)crystalline materials with a small diameter (< 2mm) - please contact us for discussion.