These include breakwater (solid or porous) impacts on wave attenuation and beach process, irregular and breaking wave impacts on sediment transport on beaches, maximum turbidite at the river estuaries and feasibility of natural based protection for coastal flooding.
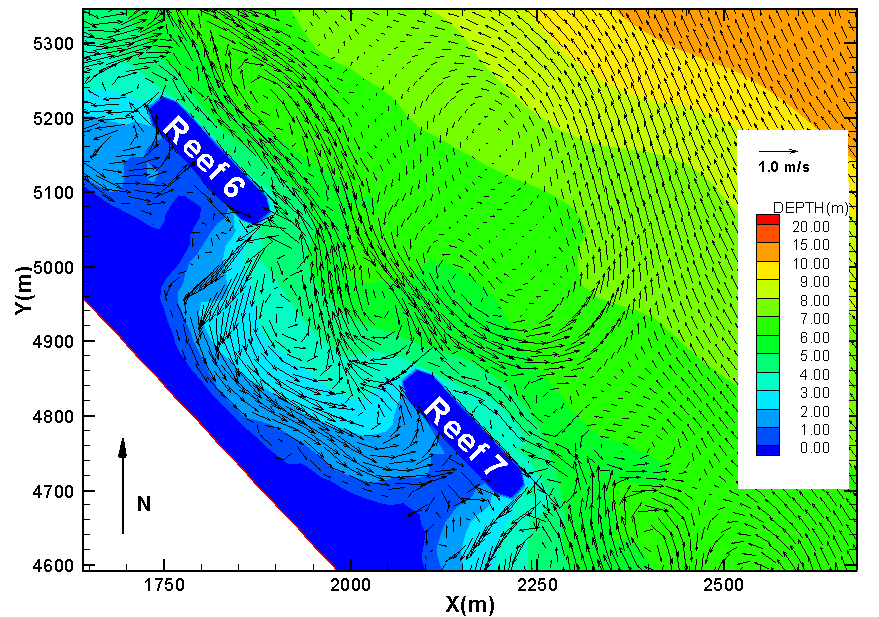
Model simulation of flow dynamics around offshore breakwaters due to combined waves and tide

Model simulated cross-shore distribution of cross-shore, alongshore and vertical Eulerian and Stokes velocities over bared beach (DUCK94) due to breaking waves.
Selected references
Zheng, P., Li, M., Wang, C., Wolf, J., Chen, X., De Dominicis, M. & Hu, Z. (2020). Tide-surge interaction in the Pearl River Estuary: A case study of Typhoon Hato. Frontiers in Marine Science, 7, 236.
Van Der Zanden, J., Cáceres, I., Larsen, B. E., Fromant, G., Petrotta, C., Scandura, P., & Li, M. (2019). Spatial and temporal distributions of turbulence under bichromatic breaking waves. Coastal engineering, 146, 65-80.
Niu, J., Xu, J., Dong, P., & Li, G. (2019). Pore water pressure responses in silty sediment bed under random wave action. Scientific reports, 9(1), 1-11.
Zhou, Y., & Dong, P. (2018). A new implementation method of sharp interface boundary conditions for particle methods in simulating wave interaction with submerged porous structure. Computers & Fluids, 177, 87-100.
Back to: School of Engineering